ASCII Code
In any computing system, data – of any type – is stored in the form of numbers. Moreover, they are represented in base 2. Consequently, to store characters in the computer, it is necessary to use a representation of characters by numbers. Such a representation is ASCII Code.
ASCII is a form of character representation in the computer used in all programming languages studied in high school, along with possibly other representations.
The standard ASCII code encodes characters using 7 bits, allowing the encoding of 27=128 characters. That's not too many! In fact, only the letters of the English alphabet, digits from 0 to 9, punctuation marks, and operators are encoded, as well as other symbols. Letters specific to other Latin alphabets (so-called diacritical letters, such as ă Ă î Î â Â ș Ș ț Ț ş Ş Ţ ţ – note that there are two kinds of Ș and two kinds of Ţ, but we will discuss this in another article), as well as letters from other alphabets: Cyrillic, Hebrew, Arabic, Chinese, etc., are completely missing. To store these letters, the Extended ASCII code or the UNICODE code can be used.
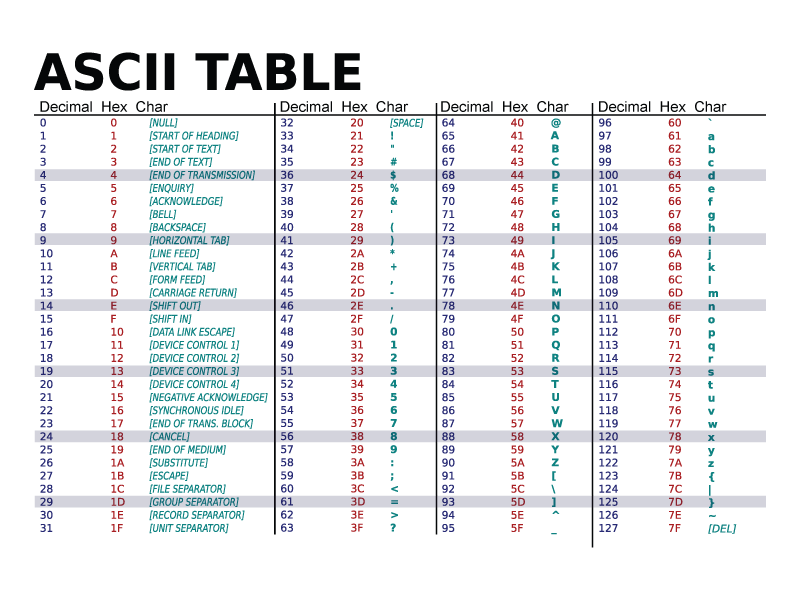
By ASCII code, each character represented in this code is associated with a number. These numbers (called ASCII codes) are in the range 0 .. 127. ASCII characters are divided into two categories:
- printable characters – those with ASCII codes in the range 32 to 126, including the boundaries: here are all the characters that have a well-defined graphic representation:
- uppercase letters: A ... Z,
- lowercase letters: a ... z,
- digits 0 .. 9,
- punctuation marks .,:;!?'"
- characters representing arithmetic or other types of operations: + - / * <> = (){}[]
- other characters: ~`@#$%^&_\|
- space character
- non-printable, or control characters – with codes 0 .. 31 and 127. They were used in the past to control data transmission. Non-printable characters do not have a well-defined graphic representation – depending on the operating system used, the graphic representations of these characters can be very different or may even be missing altogether. Among these characters, we mention two of greater importance in the programming languages studied:
- the character with code 0, also called the null character, denoted in C++ by '\0' – represents the end of a string in memory
- the character with code 10, called Line Feed, denoted in C++ by '\n' – causes a new line when displayed on the screen or in a file.
Useful Observations
- uppercase and lowercase letters are different – they have different ASCII codes
- the ASCII codes of uppercase (or lowercase) letters are in order: 'A' has the code 65, 'B' has the code 66, .. , 'Z' has the code 90. Two consecutive characters in the alphabet have consecutive ASCII codes! Also, the letter 'a' has the code 97, etc.
- the ASCII codes of lowercase letters are greater than the ASCII codes of uppercase letters ('a' > 'Z') and the difference between the ASCII codes of two letters (lowercase – uppercase) is 32.
- digits have consecutive codes: the character '0' has the code 48, the character '1' has the code 49, etc. *Note that the character '0' does not have the ASCII code 0, but 48.
- the space character is a printable character. The space has the ASCII code 32.
ASCII Table